Recently, Prof. Jie SUN’s group has published an on-line research article titled “Phytohormones-induced senescence efficiently promotes the transport of cadmium from roots into shoots of plants: A novel strategy for strengthening of phytoremediation” in Journal of Hazardous Materials (IF=7.65 in 2019). In this paper, they presented a novel strategy for strengthening of phytoremediation. Graduated student in our college, Ms. Huihui ZHU, is the first author, and associate Professor Ke CHEN and Professor Jie SUN are the co-corresponding authors of the paper. Wuhan Botanical Garden of Chinese Academy of Sciences, School of Resource and Environmental Sciences of Wuhan University and School of Water Resources and Environment of China University of Geosciences Beijing are printing affiliations of the research paper.
Link to the paper: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122080

Compared to traditional physical chemistry technology, phytoremediation is more popular as an inexpensive and environmentally friendly in-situ clean-up strategy for remediation of metal-contaminated soil. But the application of phytoremediation is limited due to time costly caused by the long growth period of plants. Therefore, developing applicable strategies to shorten the time by promoting the efficiency of phytoremediation has become a hotspot issue in the field of remediation of soils.
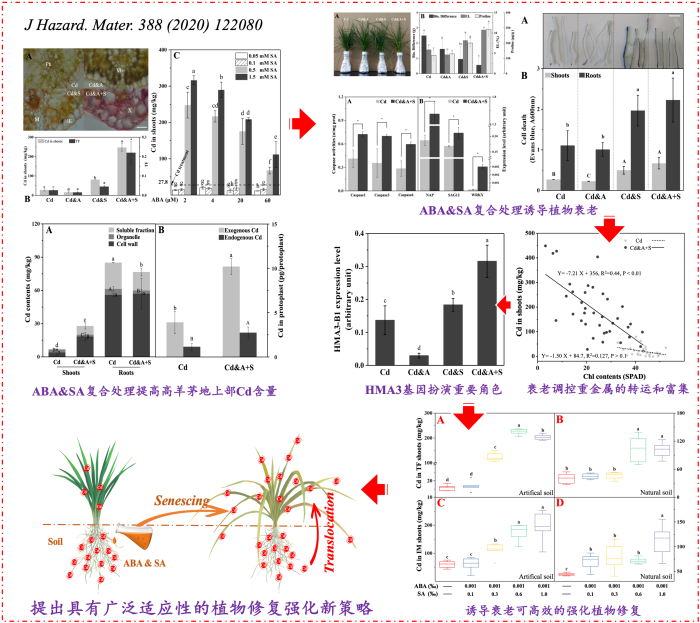
In this study, two senescence-relative phytohormones, abscisic acid (ABA) and salicylic acid (SA), were applied to strengthening phytoremediation of Cd by tall fescue (Festuca arundinacea S.). Under hydroponic culture, phytohormones treatment increased the Cd content of shoots 11.4-fold over the control, reaching 316.3 mg/kg (dry weight). Phytohormones-induced senescence contributes to the transport of heavy metals, and HMA3 was found to play a key role in this process. Additionally, this strategy could strengthen the accumulation of Cu and Zn in tall fescue shoots. Moreover, in soil pot culture, the strategy increased shoot Cd contents 2.56-fold over the control in tall fescue, and 2.55-fold over the control in Indian mustard (Brassica juncea L.), indicating its comprehensive adaptability and potential use in the field.
They first proposed the novel strategy to strengthen phytoremediation by senescence-induced heavy metal transport. The strategy could be applied at the end of phytoremediation with an additional short duration (7 days) with comprehensive adaptability, and markedly strengthen the phytoremediation in the field. And the strategy produced significant effects not only on different metals including Cd, Zn and Cu, but also on different plants including grasses and cruciferous family. The strengthening strategy provided a new method and tendency in research and application of phytoremediation in heavy metal contaminated soil.
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41503067).